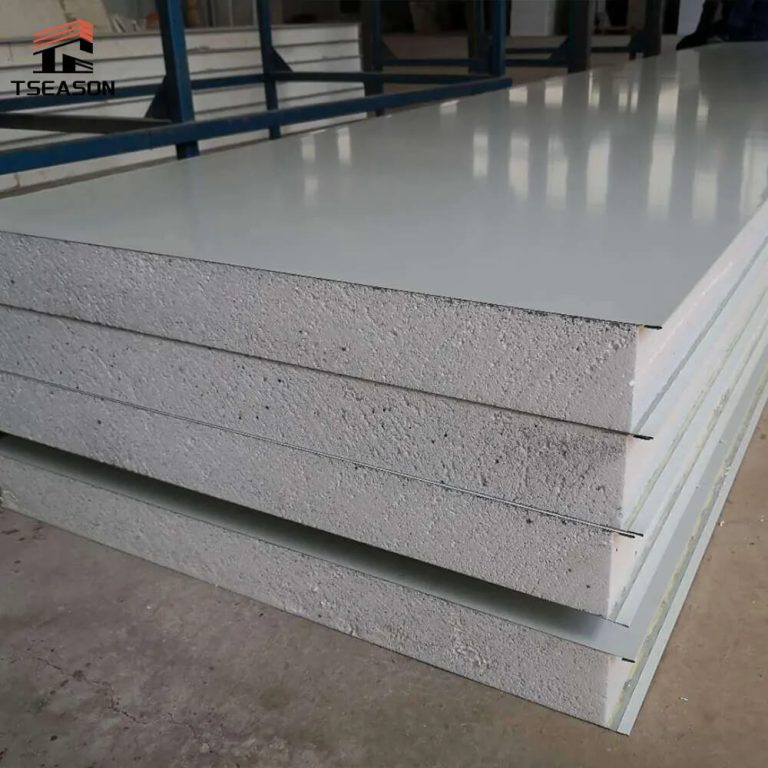
What is thermal conductivity, and What is the thermal conductivity of Tseason sandwich panels?
Date 2024.05.27
Thermal conductivity, denoted by λ, is a material's ability to conduct heat. It is the amount of heat transferred through a 1-meter-thick material with a temperature difference of 1 degree (K or °C) across its two surfaces per square meter of area in one second. The unit of thermal conductivity is watts per meter per degree Kelvin (W/m·K), which can also be represented as W/(m·K) or W/m·K (where K can be replaced with °C).
Factors Affecting Thermal Conductivity:
- Material Composition: Different materials have varying thermal conductivity values.
- Material Structure: The same material can exhibit different thermal conductivity depending on its structure, density, humidity, temperature, and pressure. In general, materials with lower water content and lower temperatures have lower thermal conductivity.
- State of Matter: Solids generally have higher thermal conductivity than liquids, and liquids have higher thermal conductivity than gases. This difference is mainly due to the varying intermolecular spacing in these states.
- Experimental Determination: Thermal conductivity values used in engineering calculations are typically obtained through specialized experimental measurements.
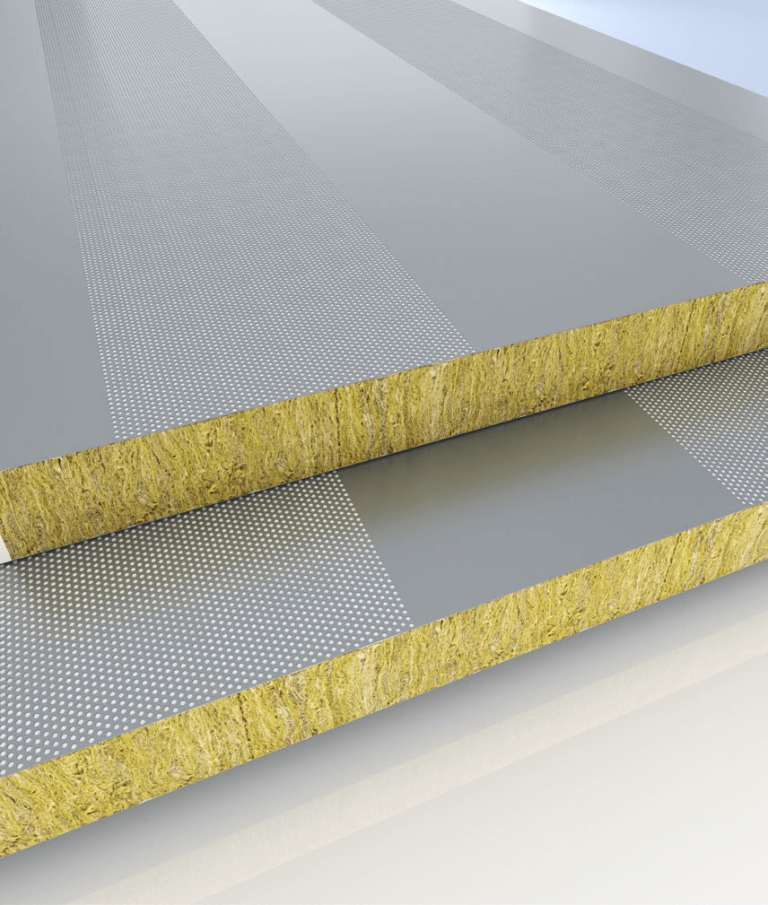
Tseason Core Material Thermal Conductivity rate is below.The lower the thermal conductivity, the better the insulation.
| Material | Rock wool | Glass Fiber | PU | PIR |
| Core Average Density (kg/m³) | 120 | 64 | 42 | 48 |
| Core Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 0.042 | 0.04 | 0.022 | 0.022 |
Realted
Products